RAID Management
Flexible RAID management, upgrade, and migration
RAID management made flexible
QNAP NAS supports various RAID types that provide varying levels of performance and data redundancy. Based on the number of hard drives of different NAS, you can choose from single; RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60; and hot spare configurations.
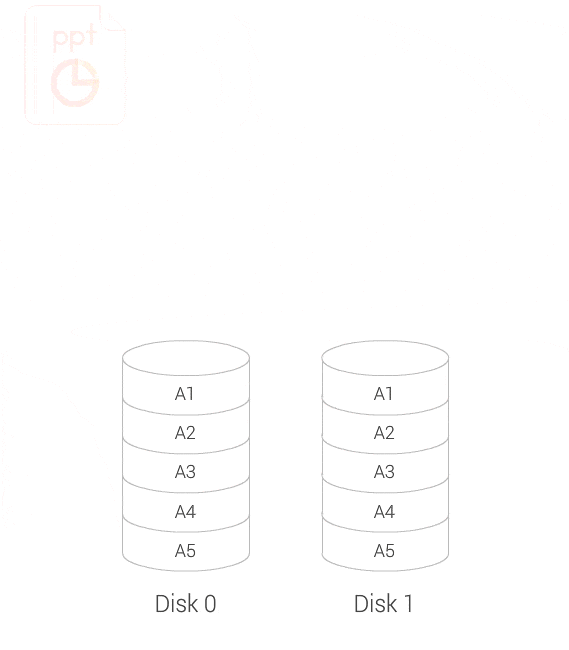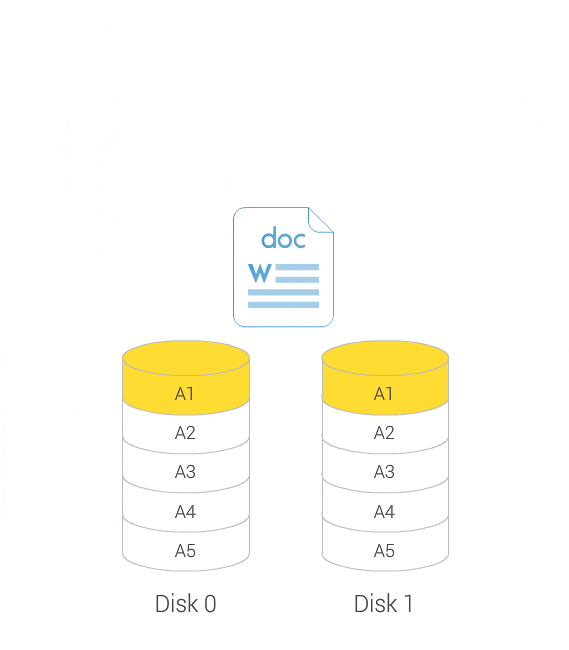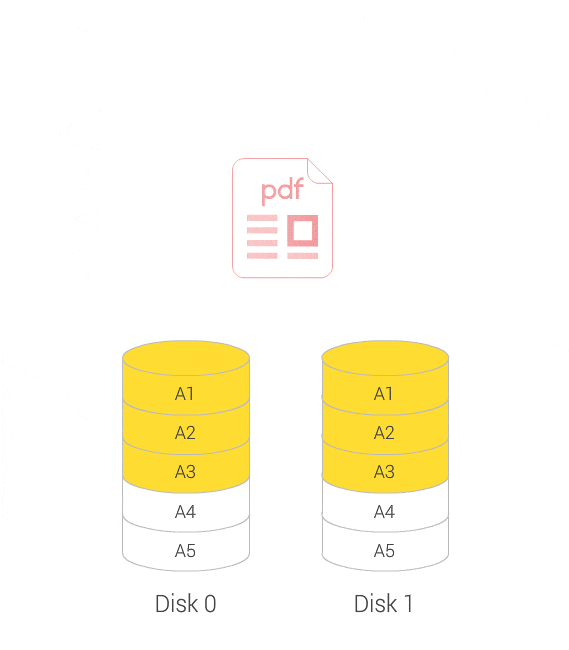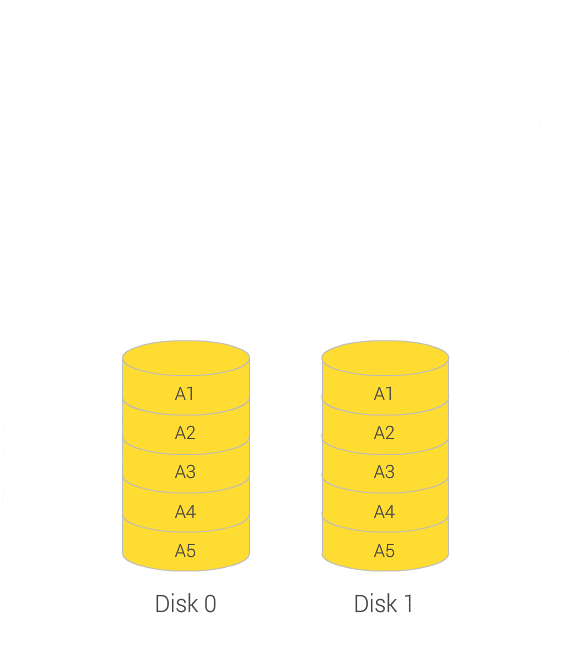
No server downtime when expanding or migrating your RAID volumes
Expand a RAID group
You can increase the maximum storage capacity of a RAID group by replacing all member disks with higher-capacity disks. This operation can be performed while the RAID group is online and accessible to users.

Change the RAID type of a RAID group
When your data grows in importance, you can migrate the system from single drive mode to RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 6 by adding additional hard drives. The migration process can be achieved without losing access to data or interrupting NAS services.
» Read the Tutorial

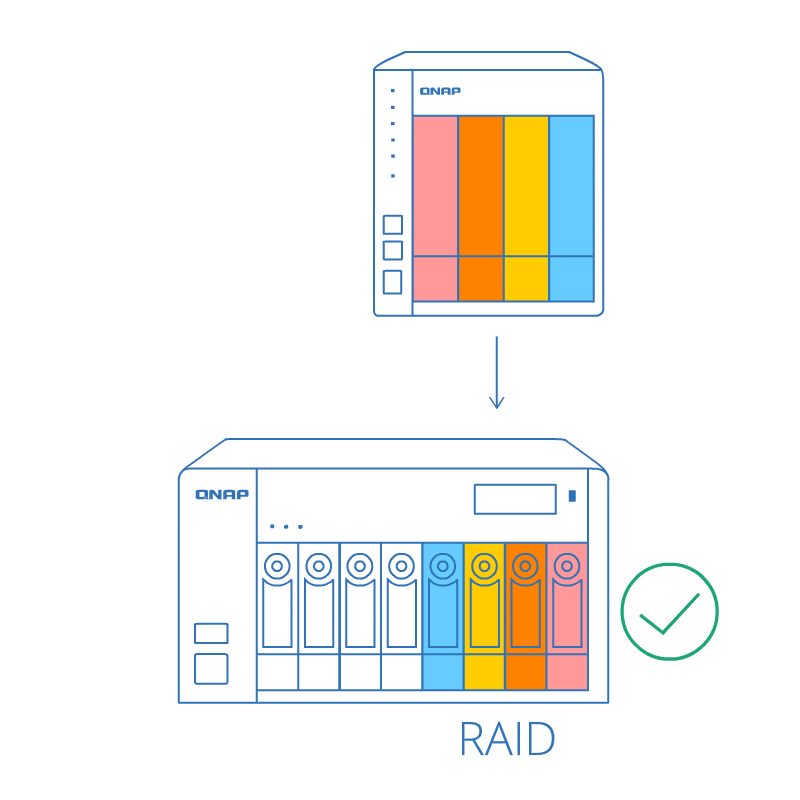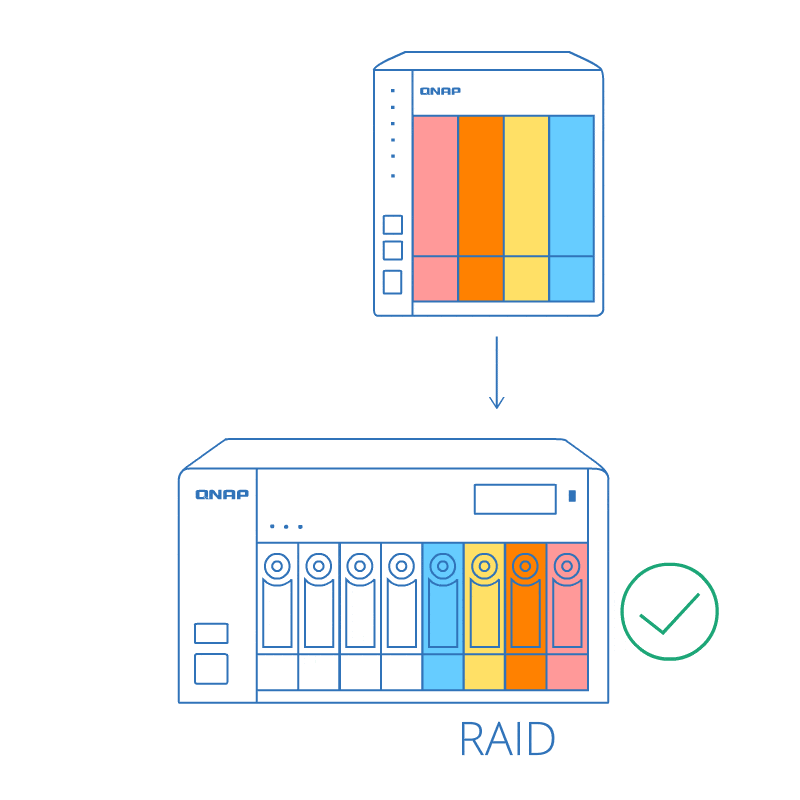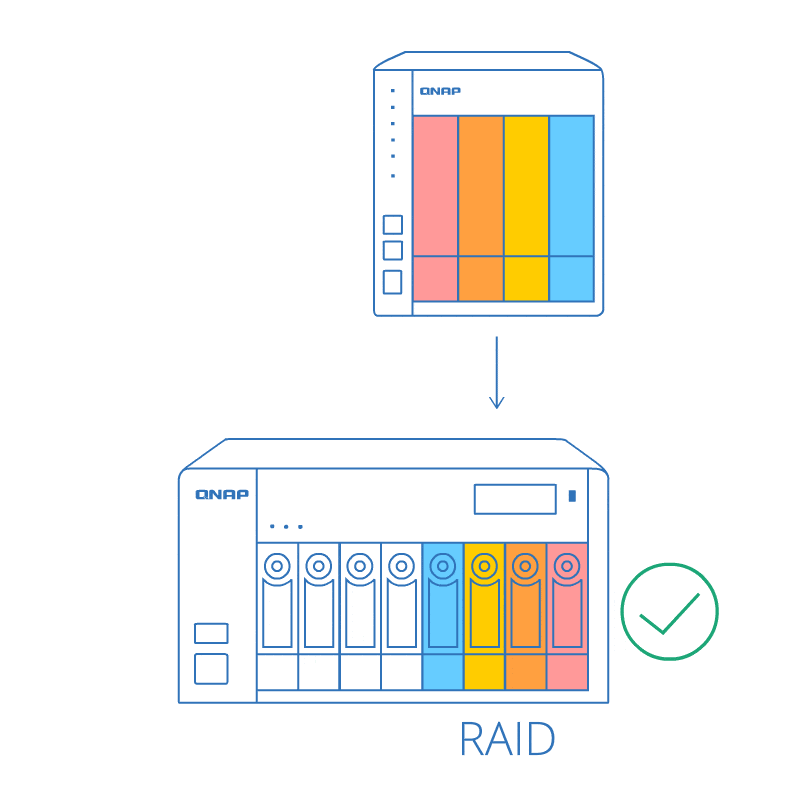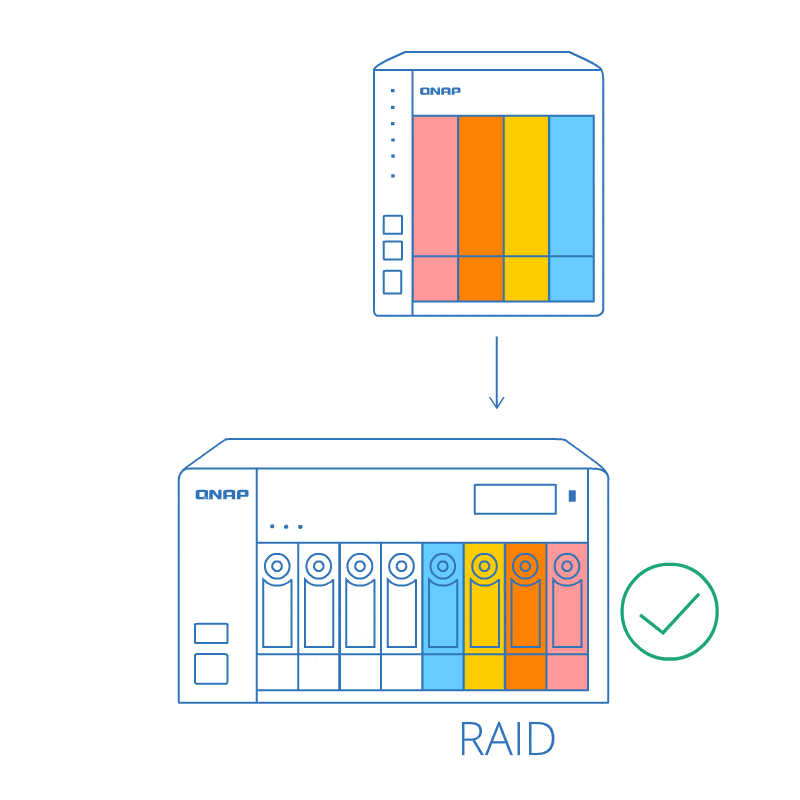
RAID order auto detection
Even if the drives are not plugged in the same sequence (while powered-off), the RAID order auto detection ensures that the data stored on the RAID can be used on the new NAS. Moving data between NAS systems becomes much easier!
RAID hot-spare and Global hot-spare drives
Assigning a hot spare gives extra protection against data loss. If a hard drive in a specific RAID group fails, the RAID group will be automatically rebuilt with the hot-spare and the remaining healthy drives to ensure continuous system operation. The global hot-spare drives can also be shared across multiple RAID groups.

Advanced RAID read error recovery technology
If read errors occur due to bad blocks on a hard drive, the correct data on the bad blocks are automatically recovered with other healthy hard drives. Users will always obtain correct data. The process is run as a background task, providing users a hassle-free experience.
Recover a RAID group
In the event of accidental disk removal or SATA connector failure, the system can recover to the degraded mode by just one-click after all the hard drives are inserted back to the system.
» Read the Tutorial